Marxism Summary Britannica
WEB Marxism Ideology and socioeconomic theory developed by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels The fundamental ideology of communism it holds that all people are entitled to enjoy the fruits of their labour but are prevented from doing so in a capitalist economic system which divides society into two classes nonowning workers and nonworking
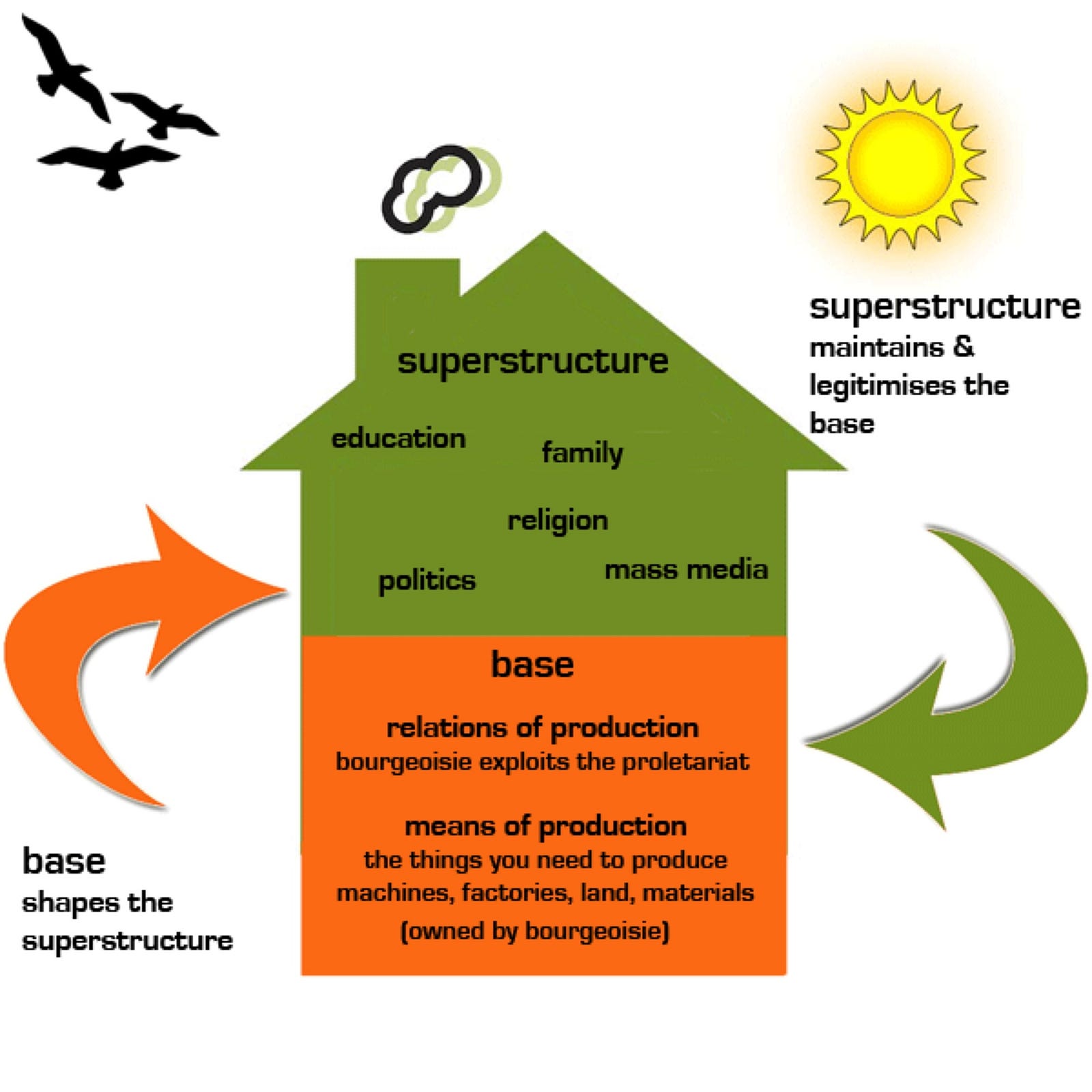
Base And Superstructure Wikipedia, WEB Marx s theory of base and superstructure can be found in the disciplines of political science sociology anthropology and psychology as utilized by Marxist scholars Across these disciplines the base superstructure relationship and the contents of

5 1 The Basics Of Marxism Social Sci LibreTexts
WEB Feb 20 2021 nbsp 0183 32 To explain Marxism in IR we need to start with Marx s main theory for the development of capitalism historical materialism Most simply historical materialism asserts that human beings including their relations with each other and their environment are determined by the material conditions in which they can survive and reproduce
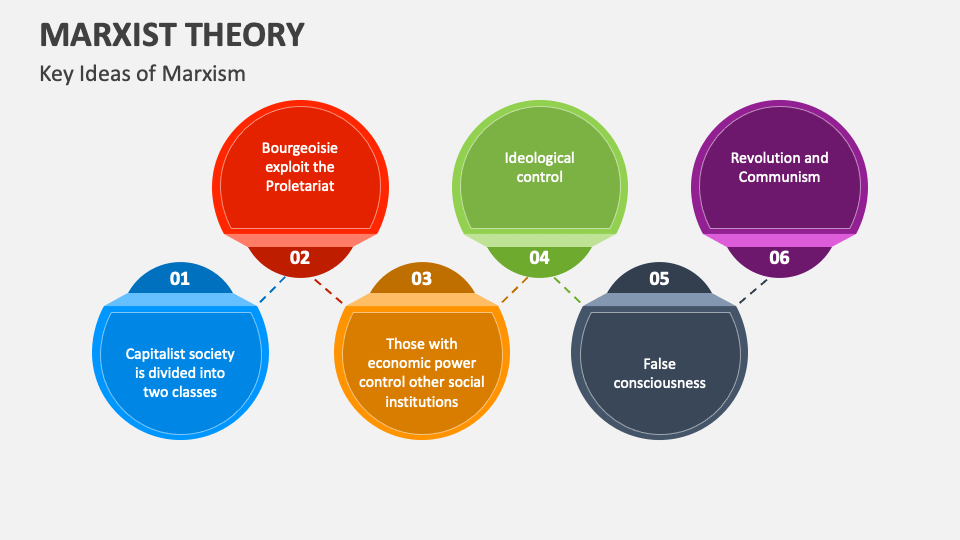
8 6E Marx s View Of Class Differentiation Social Sci LibreTexts, WEB Feb 20 2021 nbsp 0183 32 Diagram the relationship between the owners of production the proletariat the substructure and the superstructure according to Marx s view Key Points In capitalist societies the bourgeoisie class owns the means of production while the proletariat class sells their labor to the bourgeoisie

Marxist Theory Saylor Academy
Marxist Theory Saylor Academy, WEB In general terms Marxist theory can be described as an economic approach to interpreting literary texts Marxist theorists often examine literary texts with a critical eye toward their various economic ideological and social contexts suggestions and assertions Marxist theorists tend to focus their interpretations on considering how
Marxist Theory Diagram Lupon gov ph
Historical Materialism Definition Marx Examples Dialectical
Historical Materialism Definition Marx Examples Dialectical WEB Historical materialism theory of history associated with the German economist and philosopher Karl Marx and his colleague Friedrich Engels The theory postulates that all institutions of human society e g government and religion are the outgrowth of its economic activity

Superstructures New Society Medium
WEB Feb 13 2024 nbsp 0183 32 Olivia Guy Evans MSc Updated on February 13 2024 Reviewed by Saul Mcleod PhD On This Page Theory Strengths Criticisms FAQs Marxism is a social political and economic theory proposed by Karl Marx in the 19th century and Marxists are those who ascribe to the ideas of Marxism Karl Marx Sociologist Contributions And Theory Simply Psychology. WEB Summary Class Category of classification or action unit The manner of speaking of classes even with some reservation for the most part soon forgotten as if they shared interests systems of values and hence ideologies in the same way as action units do reflects the influence of historism often associated with historical and ethical WEB Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis It uses a materialist interpretation of historical development better known as quot historical materialism quot to understand class relations and social conflict It also uses a dialectical perspective to view social transformation
Another Marxist Theory Diagram you can download
You can find and download another posts related to Marxist Theory Diagram by clicking link below
- Base And Superstructure Defining Marxist Terms
- Marxism Definition Theory Examples And Criticisms
- Marxist Theory PowerPoint Presentation Slides PPT Template Lupon gov ph
- Logic Diagram 1 Of The Correlation Relationship Between Marxist Popular
- Marxism Examples Concepts Ideology Criticisms 2024
Thankyou for visiting and read this post about Marxist Theory Diagram